“Whoever hates his brother is a murderer, and you know that no murderer has eternal life abiding in him.” I John 3:15
The book of I John is about cultivating fellowship or intimacy with God and other believers in Jesus (1:1-4). The apostle John has addressed barriers to this fellowship with God which include sin (1:5-2:11; 2:29-3:10a), the world (2:15-17), and the Devil and his false teachers or antichrists (2:18-27).
Beginning in 2:28, John talks about how Christians can have more confidence and less shame before Christ at His coming (2:28-4:19). John wants his Christian readers (2:12-14; 5:13) to see themselves as children of God who possess a sinless born-again nature (God’s “seed”) at the core of their being so they will manifest God’s righteous nature by living righteously (2:29-3:10a). This righteous behavior is more than human kindness and morality that even non-Christians can manifest. It includes believing in Christ for new birth and loving one’s Christian brother or sister (3:24).
John now wants to expand upon the idea of manifesting our born-again nature (3:9) through loving fellow Christians (3:10b-23). Just as we can conceal our born-again nature by not practicing righteousness (2:29-3:10a), so we can also conceal our born-again nature by refusing to love our Christian brother (3:10b-23). In this section, John will talk about what love is not (3:10b-15) and what love is (3:16-23). Today we will look at what love is not.
“In this the children of God and the children of the devil are manifest: Whoever does not practice righteousness is not of God, nor is he who does not love his brother.” (I John 3:10). Last time in our study, we learned that only Christians can be called “children of God” since the Bible clearly says that a person who believes that Jesus is the Christ is “born of God” (5:1). The way to make their born-again nature visible to others is through practicing righteousness and loving one another as Christ commanded. Nowhere in the Bible are we told that a person is “born of the devil.” Whenever a Christian or a non-Christian sins, he or she is behaving like children of the devil since all sin is sourced in him (3:8).
When John says, “Whoever does not practice righteousness is not of God, nor is he who does not love his brother” (3:10b), the genitive phrase “is not of God” (ouk estin ek tou Theou) simply means that a Christian who does not practice righteousness nor love his Christian brother does not have actions that are sourced in God. 1 Sin can never be traced back to God regardless of who commits it. God is never responsible for sin whether it is committed by a Christian or non-Christian.
Unfortunately, the NIV translation of 3:10b does not reflect the Greek text when it says, “Anyone who does not do what is right is not God’s child, nor is anyone who does not love their brother and sister.” (I John 3:10b). Nowhere in the Greek text does it say, “God’s child.” This has been added by the translators and reflects their theological point of view, not a careful study of the Greek text.
“There is nothing in this text about not being a child of God. How could there be? One must be a child of God before one could hate his brother. An unsaved person has no Christian brother to hate (cf. 2:9) … John also moves from a broader to a narrower theme. The words whoever does not practice [lit. ‘do’] righteousness can refer to anyone who lacks righteous conduct, whether saved or unsaved. But the words he who does not love his brother introduce a specific kind of righteousness that only a Christian can manifest or fail to manifest.” 2
“By joining together the idea of righteousness (mentioned in 1 John 2:29-3:7) with love (not mentioned in vv. 2-9), John formed a bridge to a new discussion. He now considered love as the appropriate expression of the regenerate life of which he had been speaking. Love is righteousness in action.” 3
One of the biggest barriers to fellowship with God is dealing with our Christian “brother” or sister.Failure to love other Christians breaks our fellowship or closeness with the Lord. Why? Because Christ commanded us to love one another as He has loved us (John 13:34-35), and when we don’t keep that command, we have sinned against God which interrupts our fellowship with Him (I John 1:5-2:11). We cannot claim to have fellowship with God and hate our Christian brother or sister at the same time (I John 2:9-11).
John writes, “For this is the message that you heard from the beginning, that we should love one another.” (I John 3:11). From “the beginning” of their Christian experience, John’s readers heard “the message… that we should love one another.”
It is important to understand the context in which John and the other apostles heard the original command to “love one another.” It was the night before Jesus’ crucifixion when the Twelve disciples had gathered with Jesus in the Upper Room. After their supper and the washing of the disciples’ feet by Christ (John 13:1-17), Christ identified Judas as His betrayer and told him to do his work quickly (John 13:18-29), and then Judas “went out immediately” to betray the Lord Jesus (John 13:30). Judas was the only unbeliever among the disciples (cf. John 6:64, 70-71; 13:10-11; 17:12). Christ removed Judas at that time because what He was about to say was only for the ears of those who had believed in Him.
Jesus said to the believing disciples, “A new commandment I give to you, that you love one another; as I have loved you, that you also love one another. By this all will know that you are My disciples, if you have love for one another.” (John 13:34-35). The apostle John who wrote I John was also the author of the gospel of John. He wants us to understand that the command to love one another is meant for believers, not nonbelievers. Loving one another is a condition for discipleship, not salvation.
Those who claim that I John was written to a mixed audience of believers and nonbelievers to help separate the true professors from the false professors are mistakenly saying that Judas was still in the Upper Room. No. Judas had been sent out. The truth Jesus shared in the Upper Room about loving one another was given only to believers. 4
“The Upper Room truth and 1 John truth is unadulterated truth for an unadulterated audience of believers.” 5
Evans writes, “Imagine a patient claims to have the flu but has no symptoms. A doctor would say, ‘You don’t have the flu.’ Similarly, the ultimate ‘symptom’ or proof of your vertical intimacy with God is your horizontal love for his children.” 6 This is why Christ said, “By this all will know that you are My disciples, if you have love for one another.” (John 13:35).
Why is this command to love one another a barrier to fellowship with God and other Christians? Anderson writes, “Why is it so hard to love our brother? Could it be that our brother has more potential to hurt us than the world? Could it be that we expect evil from the world, but not from our Christian brother? It hurts when a Christian brother does us wrong. It hurts deeply. And we go out of our way to avoid pain.” 7
Before focusing on what love is, John now states what love is not by sharing an example of brother-to-brother hatred: “Not as Cain who was of the wicked one and murdered his brother. And why did he murder him? Because his works were evil and his brother’s righteous.” (I John 3:12). Biblical love is not like the hateful and murderous behavior that Cain exhibited toward his brother Abel (Gen. 4:2-8). When John describes Cain as “of the wicked one” (ek tou ponērou), he is not suggesting that Cain was unsaved (3:12a). 8 As with the previous genitives in 3:8, 10, this is a genitive of source which means Cain’s behavior was sourced in the “wicked one,” since Satan was “a murderer from the beginning” (John 8:44). All sin, whether by a believer or unbeliever, is traced back to the Devil since he “sinned from the beginning” (3:8).
“John uses the physical relationship between Cain and Abel as an illustration of the spiritual relationship between Christian brethren. And just as it is possible for one brother to murder his biological brother, it is possible for one Christian to murder another.” 9
Hatred toward another person is not confined to the unsaved population. Christians can also hate one another. James accused his Christian readers (James 1:1, 16-18; 2:1; et al.) of murder: “You murder and covet and cannot obtain.” (James 4:2). Why would James accuse his Christian readers of murder if it were not possible for them to commit murder? Likewise, Peter warns his Christian readers (I Pet. 1:2-9, 18-23; 2:10; et al.), “But let none of you suffer as a murderer…” (I Pet. 4:15). If it were not possible for a Christian to commit murder, then Peter just wasted his time warning them not to do so.
Christ even taught that hatred toward another believer (“his brother”) was the spiritual equivalent of spiritual murder (Matt. 5:21-22). 10 Those who deny that a Christian can hate a fellow brother or sister in Christ lack the realism of the Lord Jesus Christ and the New Testament authors.
Why did Cain murder his brother Abel (Gen. 4:8)? John tells us, “Because his works were evil and his brother’s righteous.” (I John 3:12b). Cain imitated Satan’s hateful and murderous behavior when he became envious of his “brother’s righteous” behavior and “murdered” him. God had accepted Abel’s more excellent sacrifice (firstborn of his flock of sheep which was a foreshadowing of Christ’s more excellent sacrifice – Heb. 9:11-10:18) that he offered “by faith” to please God (Heb. 11:4, 6) as opposed to Cain’s fruit of the ground offering (Gen. 4:2-5) which was not offered by faith.
Hatred is often prompted by a feeling of guilt about one’s own life compared to another person’s life. Whenever Christians feel guilty because their behavior is contrary to God’s will, they find it easier to experience hatred toward those whom they know God approves. 11 Often conflicts within churches are between those who have God’s approval and those who don’t. God uses those conflicts to manifest or make evident those who have His approval – those who are not causing the division but are promoting peace and unity (cf. I Cor. 11:19). John reminds us that such hatred toward another Christian is “of the wicked one” (I John 3:12a) in that Satan is behind such unrighteous behavior, not God.
How do we respond when another brother or sister in Christ receives a blessing from God like a new car or house, a promotion or raise at work, or public recognition? 12 Are we rejoicing with our fellow Christians when God uses their giftedness to lead many people to Christ or build up the body of Christ with their teachings or services? Or do we respond with criticism, envy, or judgmentalism? John would say the latter is “of the wicked one” (3:12). It is not “of God.”
Cain’s hateful and murderous behavior was worldly, and it should not surprise Christians to see the world hate them when they live righteously and lovingly. John writes, “Do not marvel, my brethren, if the world hates you.” (I John 3:13). The world hated Jesus and Christ warned His followers that they can expect the world to hate them when they live according to His values and not the world’s (John 15:18-19). That is a normal response to anticipate from the world. But what is abnormal is for Christians to hate one another.
“We know that we have passed from death to life, because we love the brethren. He who does not love his brother abides in death.” (I John 3:14). The only other time John used a similar phrase “have passed from death to life” (metabebēkamen ek tou thanatou eis tēn zōēn) is in John 5:24 which speaks of conversion. There Jesus said, “Most assuredly, I say to you, he who hears My word and believes in Him who sent Me has everlasting life, and shall not come into judgment, but has passed from death into life.” (John 5:24). The phrase “has passed from death into life” (metabebēken ek tou thanatou eis tēn zōēn) is the same Greek text as in I John 3:14 except for the perfect tense verb which is third person singular in John 5:24 as opposed to the first person plural in I John 3:14. Hence, some interpreters believe that I John 3:14 is saying that the way to “know” you are saved is to love your Christian brothers and sisters.
“But a phrase which is used only twice in John’s writing can hardly be said to have a fixed meaning. The context here must decide its significance. The statements of 1 John 3:14b-15 suggest that the spheres of ‘death’ and ‘life’ are here treated as experiential and determined by one’s actions. If so, the issue of conversion is not in view here.” 13
The word “know” (oida) in 3:14 is different than the word (ginōskō) John used previously in I John 2:3-5 and 3:6. Anderson writes:
“The verb ‘to know’ has numerous OT parallels parallels in which it either speaks of a special intimacy or a deeper kind of understanding. In Gen 4:1 Adam ‘knew’ his wife Eve and she conceived. Obviously, he had more than a casual knowledge of her. ‘To know’ in this case is an example of physical intimacy.
“Hosea gives us several examples of spiritual intimacy. Gomer has been unfaithful and exemplifies the unfaithfulness of Israel. Both Gomer and Israel are in covenant relationships, one with a prophet and the other with Yahweh, respectively. But after she (Gomer/Israel) has played the harlot, God claims He is going to woo her back and says to her in Hosea 2:19-20,
“’And I will betroth you to Me forever; Yes, I will betroth you to Me in righteousness and in justice, In lovingkindness and in compassion, And I will betroth you to Me in faithfulness. Then you will know the LORD.’
“This use of ‘know’ speaks of a deeper experience with the Lord than she had known before, that is, spiritual intimacy.
“And Gen 22:12 gives us another example of ‘to know’ as a deeper experience of understanding. God has asked Abraham to offer his son on the altar as a sacrifice. Abraham is obedient. Just before the knife is plunged into Isaac’s heart, the Angel of the Lord says, ‘Do not lay your hand on the lad, or do anything to him; for now I know that you fear God, since you have not withheld your son, your only son, from Me.’
“Wait a minute, didn’t the Lord know before Abraham went up the mountain what was in Abraham’s heart? Sure, He did; He was omniscient, all-knowing. But after Abraham raised the knife, God experienced Abraham’s faith on a deeper level. There was a deeper kind of understanding.
“Obviously, ‘to know’ in the OT had many uses which took the knower beyond a superficial experience. That may well be what’s going on with the meaning of know in 1 John 3:14. A new believer can have assurance that he will spend eternity with God when he dies based on God’s promises (1 John 5:13). But when he has an experience of outrageous, triumphant love (loving someone who has hurt him), he enjoys the fact that he has passed from death unto life in a fuller, deeper way.” 14
What John is telling us in I John 3:14a is that when a believer loves his or her Christian brother or sister, the passage from death into life which occurs at salvation (John 5:24) can be experienced. That is, when Christians love one another, they can experience God’s “life” or fellowship in a deeper way.
It is important to remember that eternal life emphasizes the quality not just the quantity of one’s existence. All people exist forever. But it is the quality of their existence that differs.Christians can experience an increase in the quality of their eternal life when they love other Christians now. 15
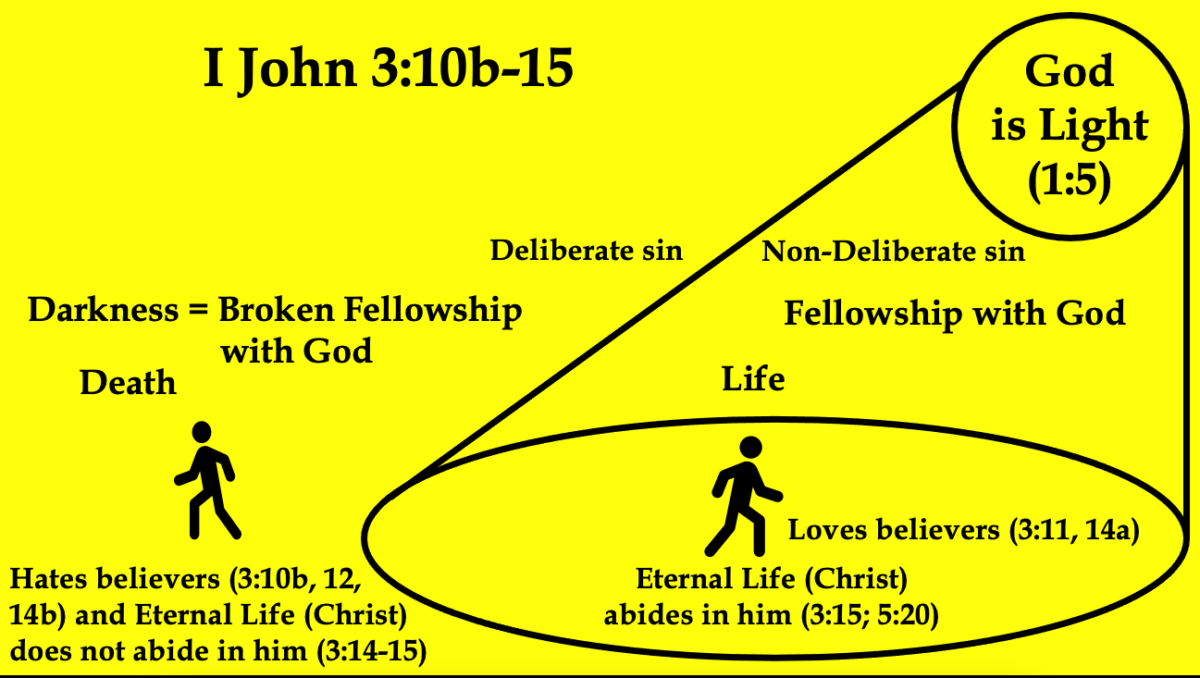
But what happens when believers do not love one another? What happens when Christians hate one another? John tells us, “He who does not love his brother abides in death.” (I John 3:14b). When a believer in Jesus refuses to “love his” Christian “brother,” it plunges him into the sphere of “death” or darkness devoid of God. Hatred toward another Christian places us in the sphere of death experientially which is the same place in which the world abides (cf. 3:13), 16 so we are no longer sharing the light with God. We are out of fellowship with God and other believers when we hate one another. As Paul stated, “For if you live according to the flesh you will die.” (Romans 8:13). The longer we hate another Christian, the more we will experience death or broken fellowship with Christ.
Remember the Greek word “abides” (menō) which means “to remain, stay, dwell, continue,” 17 is one of John’s favorite terms for fellowship or intimacy with God. In this case, abiding in the sphere of death means one is remaining out of fellowship with God. When Christians hate one another, they are no longer remaining in Christ (“life”), they are remaining in death which is devoid of Jesus. 18
When a Christian hates another Christian, that hateful “believer is out of fellowship and experiences the living death of the Christian widow who lives for pleasure (1 Tim 5:6), or the Christian miserably aware of the battle within himself between his sin(ful) nature and his desire to do what is right (Rom 7:24), or the believer whose mind is filled with things of the flesh (Rom 8:6). The believer who walks around with hatred in his heart is miserable and often depressed.” 19
Hatred of one’s Christian brother is not only an experience of “death” (3:14b), but also of murder: “Whoever hates his brother is a murderer, and you know that no murderer has eternal life abiding in him.” (I John 3:15). Some think this verse is teaching that a Christian cannot commit murder. They argue if he or she does, then they either lose their salvation or they were never saved to begin with.
I believe there is a better way to understand this verse. In the context, John is talking about how Christians can manifest their born-again righteous nature to have more confidence and less shame at the coming of Christ (2:28-29). One way is to practice righteousness (2:29-3:10a) and the other way is to love our Christian brothers and sisters (3:10b-23). In this section (3:10b-3:15), John is talking about what love is not. It is not like Cain who envied his brother Abel and murdered him (3:12; cf. Gen. 4:2-8). When a Christian hates another Christian, he is not only abiding in the realm of death or broken fellowship with God (3:14b), but he is also a “murderer” like Cain (3:12). When a Christian hates another Christian “brother,” he may not physically murder him, but he has a spirit of hatred that wants to be rid of his Christian brother, so he would not really care if he died. 20
Verse 15 does not say that “no murderer has eternal life” (as the NIRV paraphrase reads), but “that no murderer has eternal life abiding in him.” Why is this an important distinction to make? Remember, for the apostle John, eternal life is nothing more than Jesus Christ Himself. John wrote of Jesus, “1 That which was from the beginning, which we have heard, which we have seen with our eyes, which we have looked upon, and our hands have handled, concerning the Word of life— 2 the life was manifested, and we have seen, and bear witness, and declare to you that eternal life which was with the Father and was manifested to us.” (I John 1:1-2). This eternal life could be “heard… seen… looked upon” andtouched and was “with the Father and was” physically “manifested to” the apostles (1:1-2).In case you are still not convinced that eternal life is Christ, John writes, “And we are in Him who is true, in His Son Jesus Christ. This is the true God and eternal life.” (I John 5:20b).
Hence, John is not saying that a hateful Christian has lost his salvation or was never saved to begin with. He is saying that a hateful Christian is not “abiding” in Christ, that is, he is not in fellowship with Christ Who is eternal life. The moment a Christian hates another believer, he breaks experiential contact with Christ and plunges into the sphere of “death” or darkness where Christ is not. Eternal life (i.e., Christ) is not at home in his heart as long as the spirit of hatred is there. He loses his closeness with Christ, not his relationship with Him. Christians cannot abide in Christ or be close to Him and hate another believer at the same time.
Dillow writes, “Can a true Christian ‘hate his brother’? Of course, he can. David is a good example of a justified man who not only hated but followed up the murder in his heart with murder in reality by killing Uriah the Hittite (2 Samuel 12:9).” 21
Even though David had committed adultery and murder, the Bible refers to David as an example of those who are justified (declared totally righteous before God) by faith alone in Christ alone apart from any works. “5 But to him who does not work but believes on Him who justifies the ungodly, his faith is accounted for righteousness, 6 just as David also describes the blessedness of the man to whom God imputes righteousness apart from works: 7 ‘Blessed are those whose lawless deeds are forgiven, and whose sins are covered; 8 Blessed is the man to whom the Lord shall not impute sin’ ” (Romans 4:5-8; cf. 2 Sam. 12:9, 13; Psalms 32:1-2; 51). Paul quotes David (Rom. 4:7-8) who wrote in Psalm 32:1-2 of the blessedness of forgiveness as he looked ahead to the death and resurrection of Jesus Christ which would pay the penalty for the sin of the world (John 1:29), including David’s adultery and murder (cf. Psalm 16:8-11; Acts 2:24-36; Col. 2:13-14).
Paul is saying that the righteousness of Jesus Christ was credited to David and all who believed in His coming death and resurrection in the Old Testament (Rom. 4:5-8; cf. Gen. 15:6; Isaiah 61:10; John 8:56; Heb. 11:26). So, when a person in the Old Testament or in the New Testament believes in the coming Messiah, Jesus Christ, he or she is covered with the righteousness of Jesus Christ so that God no longer sees their sin, He sees the perfect righteousness of His Son (Gen. 15:6; Rom. 3:21-4:25; 2 Cor. 5:21).
“When we harbor anger in our hearts, John says, we are in effect murderers, and we abide in death, the very sphere from which we were delivered when we became Christians. We walk as ‘mere men’ (1 Corinthians 3:3), that is, as if we were still unregenerate. We are ‘carnal Christians’ who are ‘walking in darkness’ (1 John 2:11) and are in danger of losing our reward (2 John 1:8); losing what we have (Mark 4:25) and shrinking back in shame at the Judgment Seat of Christ (1 John 2:28). Jesus Christ is not at home in such a heart. He does not abide there.” 22
The love that will increase our confidence and decrease our shame at the coming of Christ (2:28) is not like Cain’s envious and murderous behavior (3:12) and the world’s (3:13), which breaks a Christian’s fellowship with Christ Who is eternal life (3:14-15; cf. 1:1-2; 5:20). When hatred occupies a Christian’s heart, it is a miserable existence. Lord Tennyson would agree:
“He that shuts Love out, in turn shall be Shut out from Love, and on her threshold lie Howling in the outer darkness.” 23
The sobering thing about harboring hatred in our hearts toward another Christian is we tend to become like the one who hurt us. The more we review the hurt that was caused to us, the more we become like that person who wounded us. This is Satan’s strategy – to get Christians to hate one another. He knows that if he can accomplish this, he will greatly diminish the church’s impact on the world for Christ.
Jesus Christ came to destroy the works of the Devil which includes hatred toward another Christian (3:8b). Christ gave us a born-again nature the moment we believed in Him for eternal life (3:9; cf. 5:1). This new nature cannot sin (3:9). The way we can express this new nature is by not hating our Christian brothers and sisters (3:10b-15). When we do hate another believer, we are abiding in darkness and death (I John 2:11; 3:14b), and out of fellowship with Christ Who is eternal life (I John 3:15; cf. 1:1-2; 5:20). To remain in this condition does not jeopardize a believer’s salvation, but it does interrupt his or her fellowship with God (I John 1:5-2:11; 3:14-15) and puts them in danger of losing eternal rewards in the future (2 John 1:8; cf. I Cor. 3:8-15).
Prayer: Gracious heavenly Father, we praise You for giving us a born-again nature the moment we believed in Jesus so You could destroy the works of the Devil. Please enable us to visibly manifest that nature by loving our Christian brothers and sisters as Jesus loved us. We cannot be close to Jesus when we harbor hatred in our hearts toward other brothers and sisters in Christ at the same time. Please O Lord, increase our love for other Christians so we can grow closer to Christ and one another. Use our love for one another to draw the unsaved to Yourself. In the mighty name of the Lord Jesus Christ, we pray. Amen.
ENDNOTES:
1. This is known as an ablative genitive of source in the Greek language. See Zane C. Hodges, The Bible Knowledge Commentary Epistles and Prophecy, Editors John F. Walvoord and Roy B. Zuck (David C. Cook, 2018 Kindle Edition), Kindle Location 3855 and Joseph Dillow, Final Destiny: The Future Reign of The Servant Kings: Fourth Revised Edition (Grace Theology Press, 2018 Kindle Edition), pg. 500.
2. Zane C. Hodges; Robert Wilkin; J. Bond; Gary Derickson; Brad Doskocil; Dwight Hunt; Shawn Leach; The Grace New Testament Commentary: Revised Edition (Grace Evangelical Society, Kindle Edition, 2019), pg. 596.
3. Hodges, The Bible Knowledge Commentary Epistles and Prophecy, Location 3856 to 3861.
4. David R. Anderson, Maximum Joy: I John – Relationship or Fellowship? (Grace Theology Press, 2013 Kindle Edition), pg. 166.
5. Ibid.
6. Tony Evans, CSB Bibles by Holman, The Tony Evans Bible Commentary (B & H Publishing Group, Kindle Edition, 2019), pp. 2943-2944.
7. Anderson, Maximum Joy, pp. 166-167.
8. Tom Constable, Dr. Constable’s Notes on I John, 2022 Edition, pg. 84.
9. Hodges, The Grace New Testament Commentary, pg. 596.
10. Hodges, The Bible Knowledge Commentary Epistles and Prophecy, Kindle Location 3883.
11. Hodges, The Grace New Testament Commentary, pg. 596.
12. Anderson, Maximum Joy, pg. 167.
13. Hodges, The Bible Knowledge Commentary Epistles and Prophecy, Kindle Location 3872 to 3877.
14. Anderson, Maximum Joy, pp. 168-169.
15. Ibid., pg. 169.
16. Hodges, The Bible Knowledge Commentary Epistles and Prophecy, Kindle Location 3892.
17. Walter Bauer, A Greek-English Lexicon of the New Testament and Other Early Christian Literature: Third Edition (BDAG) revised and edited by Frederick William Danker (Chicago: University of Chicago Press, 2000 Kindle Edition), pp. 630-631.
18. Evans, The Tony Evans Bible Commentary, pg. 2944.
19. Anderson, pg. 169.
20. Hodges, The Grace New Testament Commentary, pg. 597.
21. Dillow, Final Destiny, pg. 501.
22. Ibid.
23. Anderson, Maximum Joy, pg. 170.